1. Definition
Coating of a few nm up to 1-2
Why do we need them (add properties to substrate)
Electrical conductivity
Optical properties
Insulation
Examples
Optical: anti-reflection, interference effect
Color
Wear protection due to nanostructure (TiN)
Electrical conductors
2. Properties vs bulk material
Bulk properties : grain size influences mechanical properties
Thin films properties: mainly the prop. of the gas phase used to form the film
Coating properties: thickness, roughness, adhesion, hardness, composition, optical / electrical properties
Structural zone model
The thin film is classed into 3 categories (zones)
Influenced by substrate temperature and roughness
Activation energy for diffusion process
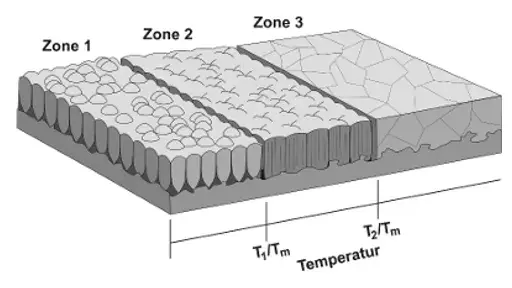
Zone 1 : rough substrate, low temp → porous coating, weak adhesion
Zone 2 : higher substrate temp → less porous, better adhesion
Zone 3: further temp. increase → diffusion of coating, modification of crystal structure
3. Residual stress
Insufficient adhesion may lead to delamination of a coating
Residual stress: compressive or tensile stress
Main cause : different shrinking coefficients between substrate and film
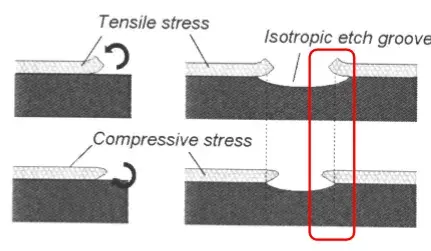
Different etching dimension from type of residual stress
Use residual stress for free-standing beams or curved mirrors