ASIC
Application specific integrated circuit
- Billions of transistors
- long design
- cost a lot : 100k … 5m
Only makes sense for high volume market
Configurable hardware
General principle
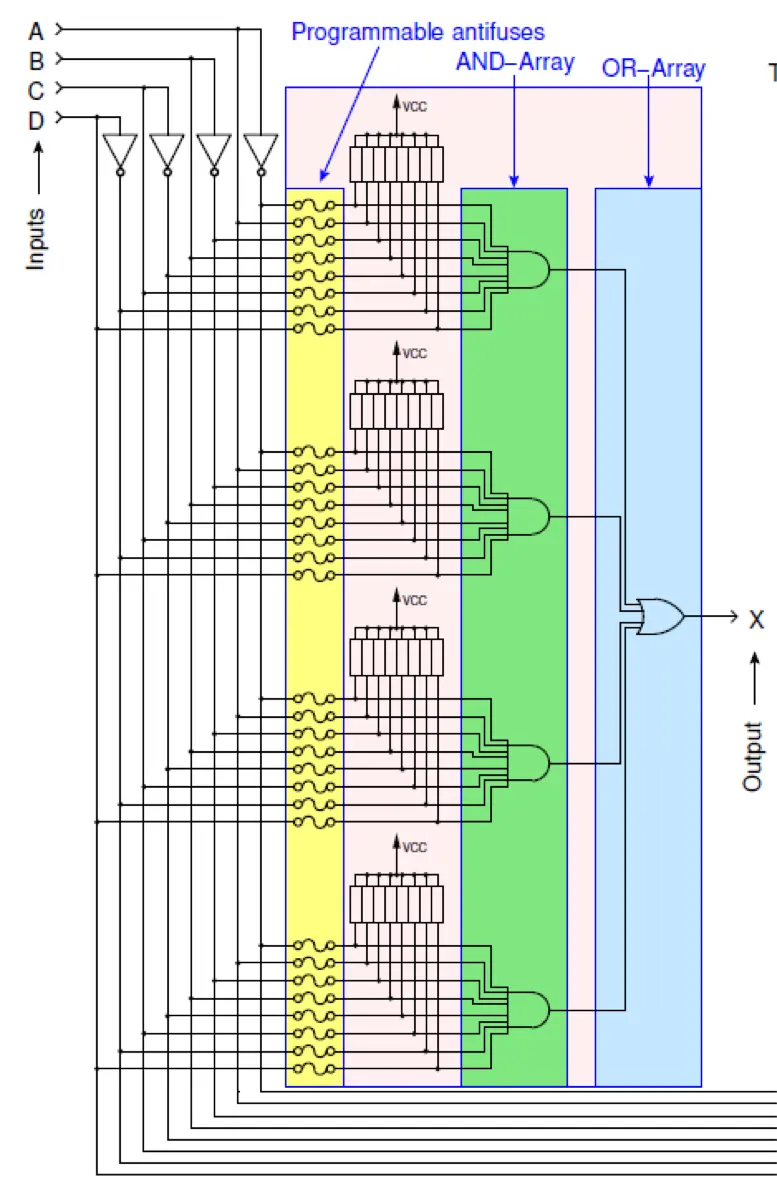
Any logic function can be expressed in the form of a sum of products (SOP, canonical form)
PAL (Programmable Array Logic)
Based on the canonical form.
✅Fixed delay, lower power, non volatile
➖ One time programmable via blown fuses
- Many many macro cells next to each other
- Fixed OR array
GAL (Generic Array Logic)
The fuses are replaced with (electrical erasable) switches: FG-MOSFETs. Same structure as PAL
✅Program last 20 years, reprogrammable 10k times
➖ No sequential logic
PLD/CPLD
Same as GAL with FG-MOSFETs but we add D-flipflops to remember the output during a clock cycle (sequential logic).
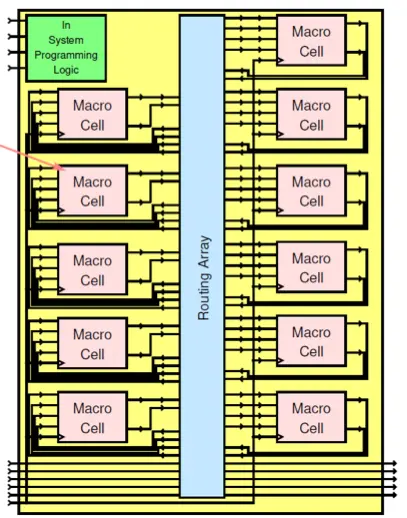
CPLDs
The routing array is a matrix of connections from macro-cells to macro-cells and outside. Each cross point has a switch
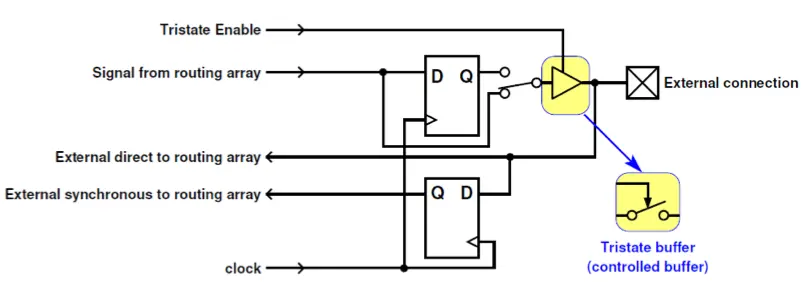
How to connect to the outside → IO block
To connect to the outside, a tristate buffer is used ,such that we can use a pin as input or output: